جلوگیری از پوسیدگی دندان
2016-01-04
نیاز به ایمپلنت های دندانی
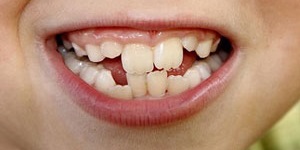
2016-01-05Tooth decay is the destruction of tooth structure and can affect both the enamel (the outer coating of the tooth) and the dentin layer of the tooth
Tooth decay occurs when foods containing carbohydrates (sugars and starches), such as breads, cereals, milk, soda, fruits, cakes, or candy are left on the teeth. Bacteria that live in the mouth digest these foods, turning them into acids. The bacteria, acid, food debris, and saliva combine to form plaque, which clings to the teeth. The acids in plaque dissolve the enamel surface of the teeth, creating holes in the teeth called cavities
To prevent tooth decay
Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a fluoride-containing toothpaste. Preferably, brush after each meal and especially before going to bed
Clean between your teeth daily with dental floss or interdental cleaners, such as the Oral-B Interdental Brush, Reach Stim-U-Dent, or Sulcabrush
Rinse daily with a fluoride-containing mouthwash. Some rinses also have antiseptic ingredients to help kill bacteria that cause plaque
Eat nutritious and balanced meals and limit snacks. Avoid carbohydrates such as candy, pretzels and chips, which can remain on the tooth surface. If sticky foods are eaten, brush your teeth soon afterwards
Check with your dentist about use of supplemental fluoride, which strengthens your teeth
Ask your dentist about dental sealants (a plastic protective coating) applied to the chewing surfaces of your back teeth (molars) to protect them from decay
Drink fluoridated water. At least a pint of fluoridated water each day is needed to protect children from tooth decay
Visit your dentist regularly for professional cleanings and oral exam
reference
related content