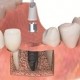
التیام بافت نرم دهان برای انجام ایمپلنت
2015-10-19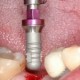
قراردهی ایمپلنت و دوباره سازی پیوند استخوان به روش هدایت شده
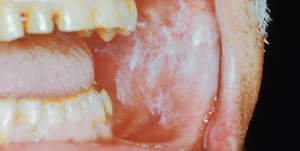
2015-10-19benign lump on tongue
Chronic irritation from smoking is the most common cause of white mucosal lesions. Because benign leukoplakic growths are virtually impossible to distinguish from carcinoma, biopsy is essential. Obtain a specimen at a nonulcerated area, using a scalpel or biting forceps and an injected or topical anesthetic
Squamous cell carcinoma is generally hyperkeratotic, but it may resemble erythroplakia, be granular, or be ulcerative with a zone of central necrosis. Lichen planus in the oral cavity is usually asymptomatic and requires no treatment, except for the erosive form, which causes pain and burning and warrants prednisone therapy (20 mg/d). Reexamine all patients with lichen planus periodically, since there is risk of transformation to squamous cell carcinoma. Several hereditary syndromes are characterized by white oral lesions; they are generally not precancerous, except for dyskeratosis congenita, which has a strong tendency to malignant transformation. Candidal infection usually presents as a thick white plaque produced by a matted collection of mycelia and desquamated epithelium. Treatment may be local (oral rinsing with nystatin suspension) or systemic,fluconazole, 100 mg/d for 7 to 10 days
Various mucosal abnormalities as well as proliferative and destructive lesions can occur in the oral cavity. Their causes include infectious agents, metabolic disorders, endocrinopathies, injuries, neoplasms, developmental abnormalities, genetic syndromes, and immunologic disturbances
Authors of textbooks and atlases on oral medicine classify these lesions according to their appearance1-3 or to the responsible agent.4,5 I find that classification based on a lesion’s appearance facilitates diagnosis, since the list of possibilities to consider is more finite
OVERVIEW OF CAUSES
White mucosal lesions may result from thickening of one or several layers of the oral epithelium. They vary in size and depth, generally have an irregular outline, and may be solitary or multifocal. Common sites are the buccal mucosa, lateral border of the tongue, floor of the mouth, and hard palate. The remainder of the tongue, soft palate, lips, and gingiva are less often involved.
Chronic inflammation heads the list of many possible causes, but genetic disorders, infectious agents, and chemical substances may also be operative. Accordingly, a complete physical examination and thorough history taking are indicated. Ask particularly about the use of prescription and over-the-counter medications. Since few lesions can be diagnosed from physical appearance alone, a biopsy is generally necessary.
Chronic irritation from all forms of smoking represents the most common cause of white mucosal lesions. Less often, the direct contact of tobacco with the oral mucosa is responsible. Snuff dipping is a potent irritant and carcinogen. Ill-fitting dentures, rough teeth, and dental restorations are also irritants.